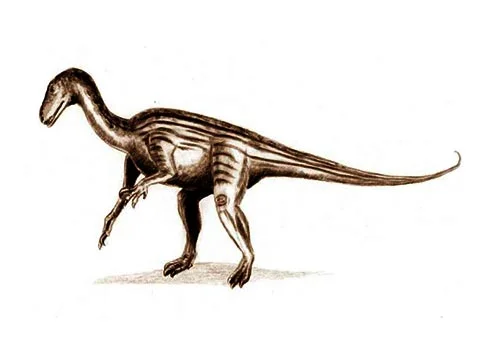
Thecodontosaurus (Socket toothed lizard)
Thee-co-don-toe-sore-us
Henry Riley & Samuel Stutchbury -1836
Herbivore/Possibly Omnivore
Estimated 1.8-3 meters long
Sauropod
T. antiquus (type)
United Kingdom, Southern England. France
Late Triassic, 200-195 million years ago
Thecodontosaurus Facts
Thecodontosaurus, also known as the “socket-toothed lizard,” is a genus of early sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 200-195 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in what is now modern-day England.
Thecodontosaurus was a small herbivorous dinosaur, measuring around 6-10 feet (1.8-3 meters) in length and weighing around 50-100 pounds (23-45 kilograms). It had a long, slender neck and tail, and long, powerful hindlimbs that suggest it was a fast runner.
The name Thecodontosaurus means “socket-toothed lizard” in reference to its unique dental arrangement, with teeth that were set into sockets in its jawbone. This type of dental arrangement is seen in many other early dinosaurs, as well as some modern reptiles, and it likely allowed for efficient chewing and grinding of plant material.
Thecodontosaurus is one of the oldest known sauropodomorph dinosaurs, a group of dinosaurs that includes some of the largest land animals to ever live. While Thecodontosaurus was relatively small, its anatomy and dental adaptations are similar to those of later, larger sauropods, suggesting that these features were already well-established early in the evolution of the group.
Thecodontosaurus likely lived in forested environments, where it would have browsed on low-growing vegetation. It may have been preyed upon by early theropod dinosaurs, although the presence of armored plates on its back may have provided some protection against predators.
The discovery of Thecodontosaurus fossils has provided important insights into the early evolution of sauropodomorph dinosaurs, and has helped paleontologists better understand the diversity and ecology of dinosaurs during the Late Triassic period. Its unique dental arrangement and other anatomical features have also shed light on the evolutionary relationships between early dinosaurs and their closest relatives.
In conclusion, Thecodontosaurus is an important early sauropodomorph dinosaur from England that lived during the Late Triassic period. Its unique dental arrangement and other anatomical features have provided valuable insights into the early evolution of sauropodomorph dinosaurs, and its presence in forested environments has contributed to our understanding of the ecology of early dinosaurs. The discovery of Thecodontosaurus fossils has also helped us better understand the diversity of dinosaurs during the Late Triassic period and the evolutionary relationships between early dinosaurs and their relatives.