Earth Time Periods
Below is a list that identifies different stages of Earth’s history. Although the list has been updated to reflect current information, please keep in mind that these dates may differ by several hundred thousand years. These temporal boundaries could be altered in the future as new techniques and studies are made and improved upon. Although there are other names that may be used for these periods, the most common are listed below.
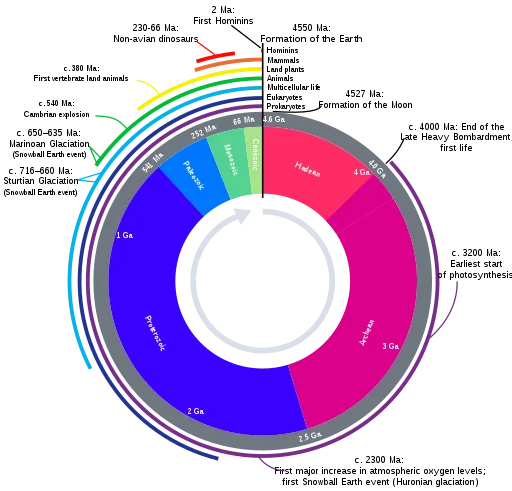
| Eon | Era | Period | Extent, millions of years ago | Duration (millions of years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phanerozoic | Cenozoic | Quaternary (Pleistocene/Holocene) | 2.588–0 | 2.588+ |
| Neogene (Miocene/Pliocene) | 23.03–2.588 | 20.4 | ||
| Paleogene (Paleocene/Eocene/Oligocene) | 66.0–23.03 | 42.9 | ||
| Mesozoic | Cretaceous | 145.5–66.0 | 79.5 | |
| Jurassic | 201.3–145.0 | 56.3 | ||
| Triassic | 252.17–201.3 | 50.9 | ||
| Paleozoic | Permian | 298.9–252.17 | 46.7 | |
| Carboniferous (Mississippian/Pennsylvanian) | 358.9–298.9 | 60 | ||
| Devonian | 419.2–358.9 | 60.3 | ||
| Silurian | 443.4–419.2 | 24.2 | ||
| Ordovician | 485.4–443.4 | 42 | ||
| Cambrian | 541.0–485.4 | 55.6 | ||
| Proterozoic | Neoproterozoic | Ediacaran | 635.0–541.0 | 94 |
| Cryogenian | 720–635 | 85 | ||
| Tonian | 1000–720 | 280 | ||
| Mesoproterozoic | Stenian | 1200–1000 | 200 | |
| Ectasian | 1400–1200 | 200 | ||
| Calymmian | 1600–1400 | 200 | ||
| Paleoproterozoic | Statherian | 1800–1600 | 200 | |
| Orosirian | 2050–1800 | 250 | ||
| Rhyacian | 2300–2050 | 250 | ||
| Siderian | 2500–2300 | 200 | ||
| Archean | Neoarchean | Not officially divided into periods | 2,800 to 2,500 million years ago | 300 |
| Mesoarchean | 3,200 to 2,800 million years ago | 400 | ||
| Paleoarchean | 3,600 to 3,200 million years ago | 400 | ||
| Eoarchean | 4,000 to 3,600 million years ago | 400 | ||
| Hadean | Not officially divided into eras | Not officially divided into periods | From formation of Earth to 4,000 million years ago | 540 |
Geological Time Scale Terminology ( Earth Time Periods Glossary )
Eon
Phanerozoic– The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 541 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period when animals first developed hard shells preserved in the fossil record.
Occurred: 541 (+/- 1) million years ago – 0 million years ago
Proterozoic – The Proterozoic is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 541 million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian “supereon.”
Occurred: 2,500 million years ago – 541 (+/- 1) million years ago
Archean – The Archean Eon is the second of four geologic eons of Earth’s history, representing the time from 4,000 to 2,500 million years ago. In this time, the Earth’s crust had cooled enough for continents to form and for the earliest known life to start.
Occurred: 4,000 million years ago – 2,500 million years ago
Hadean – The Hadean is a geologic eon of Earth history preceding the Archean. It began with the formation of the Earth about 4.6 billion years ago and ended, as defined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, 4 billion years ago. As of 2016, the ICS describes its status as “informal”
Occurred: 4,600 million years ago – 4,000 million years ago
Era
Cenozoic – The Cenozoic is Earth’s current geological era, representing the last 66 million years of Earth’s history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents.
Occurred: 66 million years ago – 0 million years ago
Mesozoic – The Mesozoic Era, also called the Age of Reptiles and the Age of Conifers, is the second-to-last era of Earth’s geological history, lasting from about 252 to 66 million years ago and comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods.
Occurred: 251.902 (+/- 0.24) million years ago – 65 million years ago
Paleozoic – The Paleozoic Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods: the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian.
Occurred: 541 (+/- 0.4) million years ago – 251.902 (+/- 0.024) million years ago
Neoproterozoic – The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 541 million years ago. It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran Periods.
Occurred: 1,000 million years ago – 541 (+/- 1) million years ago
Mesoproterozoic – The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from 1,600 to 1,000 million years ago. The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth’s history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era, but little is known about them.
Occurred: 1,600 million years ago – 1,000 million years ago
Paleoproterozoic – The Paleoproterozoic Era, spanning the time period from 2,500 to 1,600 million years ago, is the first of the three sub-divisions of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth’s geological history. It was during this era that the continents first stabilized.
Occurred: 2,500 million years ago – 1,600 million years ago
Neoarchean – The Neoarchean is the last geologic era in the Archean eon that spans from 2.8 to 2.5 billion years ago— the period being defined chronometrically and not referencing a specific level in a rock section on Earth. The era is marked by major developments in complex life and continental formation.
Occurred: 2,800 million years ago – 2,500 million years ago
Mesoarchean – The Mesoarchean is a geologic era in the Archean Eon, spanning 3,200 to 2,800 million years ago, which contains the first evidence of modern-style plate subduction and expansion of microbial life. The era is defined chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level in a rock section on Earth.
Occurred: 3,200 million years ago – 2,800 million years ago
Paleoarchean – The Paleoarchean, also spelled Palaeoarchaean, is a geologic era within the Archaean Eon. The name derives from Greek “Palaios” ancient. It spans the period of time 3,600 to 3,200 million years ago. The era is defined chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level of a rock section on Earth.
Occurred: 3,600 million years ago – 3,200 million years ago
Eoarchean – The Eoarchean is the first era of the Archean Eon of the geologic record for which the Earth has a solid crust. It spans 400 million years from the end of the Hadean Eon 4 billion years ago to the start of the Paleoarchean Era 3600 Mya.
Occurred: 4,000 million years ago – 3,600 million years ago
Periods
Quaternary (Pleistocene/Holocene) – The Quaternary is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present.
Occurred: from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present
Neogene (Miocene/Pliocene) – The Neogene is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period 23.03 million years ago to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period 2.58 Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene.
Occurred: 23.03 million years ago – 2.58 million years ago
Paleogene (Paleocene/Eocene/Oligocene) – The Paleogene is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period 66 million years ago to the beginning of the Neogene Period 23.03 Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon.
Occurred: 66 million years ago – 23.03 million years ago
Cretaceous – The Cretaceous is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago. It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic.
Occurred: 145.5 million years ago – 66 million years ago
Jurassic – The Jurassic is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period 201.3 million years ago to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 Mya.
Occurred: 201.3 (+/- 0.2) million years ago – 145 million years ago
Triassic – The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago, to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era.
Occurred: 251.902 (+/- 0.024) million years ago – 201.3 (+/- 0.2) million years ago
Permian – The Permian is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period 298.9 million years ago, to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era.
Occurred: 298.9 (+/- 0.15) million years ago – 251.902 (+/- 0.024) million years ago
Carboniferous (Mississippian/Pennsylvanian) – The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago, to the beginning of the Permian Period, 298.9 million years ago.
Occurred: 358.9 (+/- 0.4) million years ago – 298.9 (+/- 0.15) million years ago
Devonian – The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, 419.2 million years ago, to the beginning of the Carboniferous, 358.9 Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
Occurred: 419.2 (+/- 3.2) million years ago – 358.9 (+/- 0.4) million years ago
Silurian – The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago, to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era.
Occurred: 443.8 (+/- 1.5) million years ago – 419.2 (+/- 3.2) million years ago
Ordovician – The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya.
Occurred: 485.4 (+/- 1.9) million years ago – 443.8 (+/- 1.5) million years ago
Cambrian – The Cambrian Period was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 55.6 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 541 million years ago to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 485.4 mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux.
Occurred: 541 (+/- 1) million years ago – 485.4 (+/- 1.9) million years ago
Ediacaran – The Ediacaran Period is a geological period that spans 94 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago, to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 541 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon.
Occurred: 635 million years ago – 541 (+/- 1) million years ago
Cryogenian – The Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from 720 to 635 million years ago. It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran.
Occurred: 720 million years ago – 635 million years ago
Tonian – The Tonian is the first geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era. It lasted from 1000 to 720 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined by the ICS based on radiometric chronometry. The Tonian is preceded by the Stenian Period of the Mesoproterozoic Era and followed by the Cryogenian.
Occurred: 1,000 million years ago – 720 million years ago
Stenian – The Stenian Period is the final geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from 1200 Mya to 1000 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The name derives from narrow polymetamorphic belts formed over this period.
Occurred: 1,200 million years ago – 1,000 million years ago
Ectasian – The Ectasian Period is the second geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from 1400 Mya ago to 1200 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. Geologically the name refers to the continued expansion of platform covers during this period.
Occurred: 1,400 million years ago – 1,200 million years ago
Calymmian – The Calymmian Period is the first geologic period in the Mesoproterozoic Era and lasted from 1600 Mya to 1400 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically.
Occurred: 1,600 million years ago – 1,400 million years ago
Statherian – The Statherian Period is the final geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from 1800 Mya to 1600 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The period was characterized on most continents by either new platforms or final cratonization of fold belts.
Occurred: 1,800 million years ago – 1,600 million years ago
Orosirian – The Orosirian Period is the third geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from 2050 Mya to 1800 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The later half of the period was an episode of intensive orogeny on virtually all continents.
Occurred: 2,050 million years ago – 1,800 million years ago
Rhyacian – The Rhyacian Period is the second geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from 2300 Mya to 2050 Mya. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The Bushveld Igneous Complex and some other similar intrusions formed during this period.
Occurred: 2,300 million years ago – 2,050 million years ago
Siderian – The Siderian Period is the first geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from 2500 Ma to 2300 Ma. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The deposition of banded iron formations peaked early in this period.
Occurred: 2,500 million years ago – 2,300 million years ago
